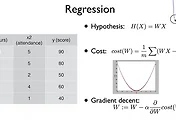
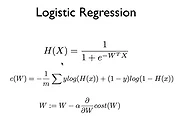지난 이론시간에 Multivariable example 을 이용한 linear regression을 학습했습니다.
좋은 성과를 내기 위해서는 적절한 feature 을 뽑아내는게 중요하다고 했었죠.
어려운건 없고 단지 feature 가 여러개일 뿐입니다.
두개의 weight를 학습해야 한다고 해봅시다.
코드는 다음과 같이 할 수있겠죠?
이런 방식으로 여러개의 W에 대한 linear regression 이 가능해집니다!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | import tensorflow as tf x1_data = [1,0,3,0,5] x2_data = [0,2,0,4,0] y_data = [1,2,3,4,5] #Try to find values for W and b that compute y_data = W * x_data + b # (We know that W should be 1 and b 0, but Tensorflow will) # figure that our for us.) W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0)) W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0)) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0)) #Our hypothesis hypothesis = W1 * x1_data + W2*x2_data +b #Simplified cost function cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data)) #Minimize a = tf.Variable(0.1) # Learning rate, alpha optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(a) train = optimizer.minimize(cost) #Before starting, initialize the variables. We will 'run' this first. init = tf.initialize_all_variables() #Launch the graph. sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) #Fit the line. for step in xrange(2001): sess.run(train) if step % 20 == 0: print step, sess.run(cost), sess.run(W1), sess.run(W2), sess.run(b) | cs |
해당 코드를 실행하면 처음에는 다음과 같이 random 한 값이 주어집니다.
하지만 결국 X1 = 1, X2 = 1, b = 0 에 수렴하는것 알 수 있습니다.
이번에는 이 복잡한 수식을 Matrix 로 표현해볼까요?
W data 를 1x2 배열로 구현한다!
matmul 은 두 행렬의 곱을 나타낸다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | import tensorflow as tf x_data = [[0., 2., 0., 4.,0.], [1., 0., 3., 0., 5.]] y_data = [1, 2, 3, 4,5] # Try to find values for W W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1,2],-1.0,1.0)) b = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0)) #our hypothesis # matrix multiplication hypothesis = tf.matmul(W, x_data) + b # Simplified cost function cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data)) #Minimize a = tf.Variable(0.1) # Learning rate, alpha optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(a) train = optimizer.minimize(cost) #Before starting, initialize the variables. We will ' run' this first. init = tf.initialize_all_variables() #Launch the graph. sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) #Fit the line. for step in xrange(2001): sess.run(train) if step % 20 == 0: print step, sess.run(cost), sess.run(W), sess.run(b) | cs |
실행하면 다음과 같이 이차원의 형태로 출력되는 것을 알 수있다.
동일하게 3개의 변수를 갖도록 해봅시다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | import tensorflow as tf x_data = [[1., 1., 1., 1.,1.], [0., 2., 0., 4., 0.], [1., 0., 3., 0., 5.]] y_data = [1, 2, 3, 4,5] # Try to find values for W W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1,3],-1.0,1.0)) #our hypothesis # matrix multiplication hypothesis = tf.matmul(W, x_data) # Simplified cost function cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypothesis - y_data)) #Minimize a = tf.Variable(0.1) # Learning rate, alpha optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(a) train = optimizer.minimize(cost) #Before starting, initialize the variables. We will ' run' this first. init = tf.initialize_all_variables() #Launch the graph. sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) #Fit the line. for step in xrange(2001): sess.run(train) if step % 20 == 0: print step, sess.run(cost), sess.run(W) | cs |
실행 결과는 다음과 같이 되겠죠?
마지막으로 Loading data from file 을 배워봅시다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np xy = np.loadtxt('train.txt', unpack = True, dtype = 'float32') x_data = xy[0:-1] y_data = xy[-1]; | cs |
다음과 같이 하면 텍스트파일에서 읽어올 수 있습니다.
C 의 freopen과 같다고 할 수가 있겠죠?
'머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [실습] 모두의딥러닝 - Logistic Classification 을 Tensorflow로 구현해보자! (0) | 2017.02.15 |
|---|---|
| [강의]시즌1 딥러닝의기본 - Logistic (regression) classification에 대해 알아보자 (0) | 2017.02.15 |
| [실습] 모두의딥러닝 - linear regression의 cost 최소화의 Tensorflow를 구현해보자! (0) | 2017.02.15 |
| [실습] 모두의딥러닝 - tensorflow로 간단한 linear regression을 구현해보자! (0) | 2017.02.10 |
| [실습] 모두의딥러닝 - tensorflow의 기본 및 설치방법 (0) | 2017.01.23 |